InDesign is a robust desktop publishing software that empowers users to design diverse print and digital media. One of its standout features is support for plug-ins—additional modules that extend its functionality. For businesses seeking tailored solutions, InDesign plugin development services provide the perfect opportunity to customize workflows, automate repetitive tasks, and unlock enhanced features. Whether you want to collaborate with an InDesign plugin development company or are looking to hire InDesign plugin developers, understanding the available options and technologies is crucial. Below, we’ll explore various methods to develop plug-ins for InDesign with code samples.
1. ExtendScript
ExtendScript, a JavaScript-based scripting language, is ideal for developers seeking to create plug-ins quickly and efficiently. It provides access to InDesign’s internal objects such as documents, pages, and text frames. For example, here’s how you can use ExtendScript to create a new document in InDesign:
javascript code:
var myDocument = app.documents.add();
Create Custom InDesign Plugins
Looking to build a tailored InDesign plugin for your workflow? Book a consultation today to explore how our developers can bring your plugin ideas to life.
ExtendScript is a great starting point for those new to InDesign plugin development services, as it simplifies basic customizations and automation.
2. InDesign SDK
For more advanced development, the InDesign SDK (Software Development Kit) is the way to go. Using C++, developers can gain deeper control and flexibility to create powerful plug-ins. For example, this C++ snippet adds a custom menu item to InDesign:
c++ code:
#include "InDesignSDK.h"
void MyPlugin::AddMenuItem() {
CAlert::Information("MyPlugin: Adding menu item");
InterfacePtr<IPanelControlData> panelData(Utils<IPalettePanelUtils>()->CreatePalettePanel(
kApplicationWorkspaceBoss,
kMyPluginPanelWidgetID,
kMyPluginPanelTitleKey,
kVerticalLayout,
kPluginMenuGroup,
kPluginMenuItemID));
panelData->AttachToMenu(kApplicationWorkspaceMenu, kBeforeAdobeOnlineServicesMenuItem);
}
For companies seeking robust and scalable plug-ins, partnering with an InDesign plugin development company experienced in SDK implementation is essential.
3. InDesign Server
For large-scale automation and batch processing, InDesign Server enables the creation of plug-ins using JavaScript, VBScript, or AppleScript. Here’s an example of a JavaScript snippet to import a CSV file and create a table in InDesign:
javascript code:
var myCSVFile = File.openDialog("Select a CSV file to import", "comma-separated values (*.csv)");
var myTable = myDocument.pages[0].textFrames.add().tables.add();
myTable.convertTextToTable(myCSVFile);
This approach is perfect for businesses needing server-based automation solutions as part of their InDesign plugin development services.
4. InDesign Scripting DOM
The InDesign Scripting DOM (Document Object Model) offers a high-level scripting interface for developers familiar with JavaScript. Here’s an example to change the color of a text frame in InDesign:
javascript code:
var myTextFrame = app.activeDocument.pages[0].textFrames[0];
myTextFrame.fillColor = "Red";
This method is efficient for scripting and streamlining everyday workflows.
5. InDesign Plugin Builder
The InDesign Plugin Builder is a graphical tool that simplifies SDK-based plug-in creation. With its drag-and-drop interface, developers can easily build complex plug-ins without extensive coding knowledge.
Steps to create a plug-in that adds a menu item:
- Open the InDesign Plugin Builder and select “New Plug-in Project.”
- Name the project and set the location.
- Add a new menu item via the GUI.
- Assign the menu item a name and ID.
- Save and build the plug-in.
This tool is highly recommended for developers looking for an intuitive entry into InDesign plugin development.
6. HTML5-Based Extensions
InDesign supports HTML5-based extensions, developed using HTML, CSS, and JavaScript. These extensions are cross-platform and can be deployed via Adobe’s Creative Cloud Marketplace. Here’s an example to create a simple panel:
html code:
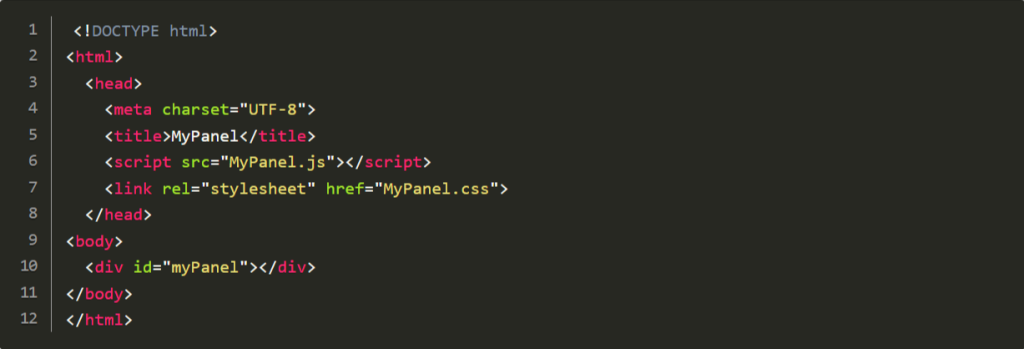
javascript:
var panel = document.getElementById("myPanel");
var myButton = document.createElement("button");
myButton.innerText = "Click me!";
myButton.onclick = function() {
alert("Button clicked!");
};
panel.appendChild(myButton);
If you’re looking to hire InDesign plugin developers for cross-platform solutions, this is an excellent approach.
7. Python Scripting
For developers familiar with Python development services, InDesign provides scripting support. Python can be used for automation or creating plug-ins. Here’s an example of changing the text frame color using Python:
python code:
import win32com.client
app = win32com.client.Dispatch("InDesign.Application")
myDocument = app.ActiveDocument
myTextFrame = myDocument.Pages[0].TextFrames[0]
myTextFrame.FillColor = app.RGBColor(255, 0, 0)
8. InDesign CC Libraries
CC Libraries enable sharing of assets across Creative Cloud applications. Developers can automate asset management with custom plug-ins. Here’s an example to add a graphic to a CC Library:
javascript code:
var myLibrary = app.libraries.itemByName("MyLibrary");
var myGraphic = myLibrary.assets.add(app.activeDocument.pages[0].graphics[0], "MyGraphic");
alert("Graphic added to CC Library!");
9. Third-Party Libraries
Several third-party libraries simplify InDesign plugin development:
- Adobe ExtendScript Toolkit SDK: Debugging ExtendScript code.
- ScriptUI: Simplifies UI creation for ExtendScript.
- InTools: Advanced utilities for InDesign.
Why Choose Professional InDesign Plugin Development Services?
Collaborating with a specialized InDesign plugin development company ensures access to experienced developers who understand the nuances of the platform. Whether you want to automate workflows, enhance user productivity, or add unique features, hiring InDesign plugin developers can make your vision a reality.
Conclusion
InDesign offers a wide range of tools for plug-in development, including ExtendScript, InDesign SDK, Server, Scripting DOM, Plugin Builder, HTML5-based extensions, Python scripting, CC Libraries, and third-party libraries. Each approach caters to specific needs, enabling developers to customize and optimize workflows.
For businesses looking to maximize their use of InDesign, partnering with an InDesign plugin development company or choosing to hire InDesign plugin development experts can help achieve unparalleled results. Custom plug-ins unlock a world of possibilities, enhancing productivity and expanding InDesign’s capabilities.
Related Keyphrase:
#InDesignPlugins #InDesignDevelopment #PluginDevelopment #AdobeInDesign #InDesignScripting #CustomPlugins #InDesignAPI #AdobeCreativeSuite #CreativeAutomation #InDesignExtensions #InDesignAPIIntegration #TechSolutions #PluginDevelopmentServices #InDesignAutomation #HireInDesignDevelopers #InDesignCustomization #InDesignExperts #CustomAppDevelopment #InDesignServices #CreativeServices #HireAdobeDevelopers #InDesignSolutions #AdobePlugins #PluginIntegration #AppDevelopmentCompany #SoftwareDevelopment #CreativeTech #DesignAutomation #AppDevelopmentServices #InDesignPluginDevelopment #InDesignTech #AdobeDevelopmentCompany #TechConsulting #CreativeProcessAutomation #InDesignDevelopmentCompany #SoftwareCustomization #AppSolutions #TechInDesign #DesignTools #InDesignExtensionsDevelopment



